Navigating the world of business finance often involves understanding various financial instruments, two of which are the Letter of Credit and the Bank Guarantee. These tools are essential for trade facilitation and risk minimization, especially in international transactions. While they may appear similar, their functions, usage, and features differ significantly. This blog aims to demystify these instruments, revealing the differences and functions they fulfill in business transactions.
What is a Bank Guarantee?
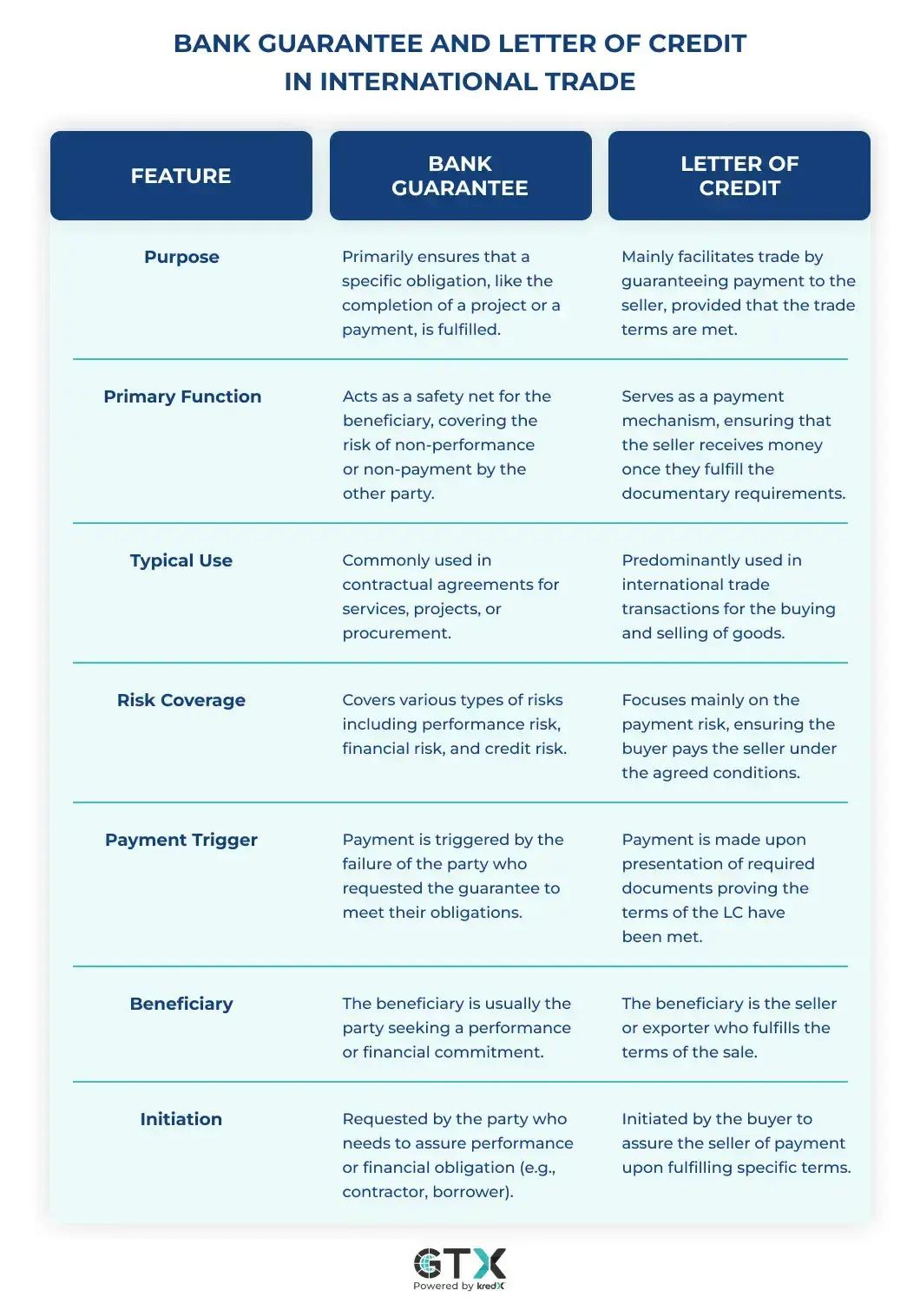
A Bank Guarantee is a document issued by any financial institution or bank promising to accomplish an obligation on the part of the beneficiary. Above all, it’s a mechanism through which the bank guarantees that the financial obligations of debtors (normally business or individual) will be fulfilled if a debtor does not repay or fulfill the contractual obligation, then the bank takes over to make up for the loss. This assurance serves as a safety net for businesses, especially in cases where there is a high-risk level. For instance, in the case when a company undertakes a large-scale work project, a Bank Guarantee can assure that either completion or failure will be compensated.
A Bank Guarantee has more uses than merely to compensate for any financial loss. It also helps businesses become more credible in the eyes of partners, suppliers, and customers. In a business atmosphere where trust is crucial, the Bank Guarantee serves as evidence of an enterprise’s reliability and financial soundness. This is particularly crucial in international trade where firms depend on guarantees to provide security for contracts and ensure that parties have complied with the terms of agreement. The role that Bank Guarantees play in smoothing out the conduct of business transactions and promoting productive commercial relations is evident when it offers this level of certainty.
Types of Bank Guarantee
Bank Guarantees have many different forms, each designed to satisfy various needs in business transactions. It is essential to know these various types as businesses need an appropriate one for their requirements.
Here's a detailed look at the most common types of Bank Guarantees:
1. Performance Guarantee
Performance Guarantee is often used in project agreements. It guarantees that the contractor will meet his obligations as stated in their contracts, especially about quality and time. In case the contractor does not meet his end of the bargain, he will be compensated by the bank on behalf of the project holder. This guarantee is an important one in the construction and manufacturing industries, where completion according to specifications counts for much.
2. Financial Guarantee
This guarantee is commonly intended to warrant the repayment of loans and financial claims. If the borrower fails to repay promptly, the bank will step up with a guarantee of settling the outstanding balance. It is especially helpful in situations where transactions have high values or when the borrower’s credibility is questionable.
3. Advance Payment Guarantee
This guarantee protects the payer at all times when an advance payment has been made for a specified activity. It guarantees that the initial payment will be refunded in case of failure by the receiving party to pursue his obligations under the contract. This is a common practice in international trade and large-scale purchase contracts.
4. Bid Bond Guarantee
A bid bond guarantee acts as a provision of security wherein if selected during tendering, a bind will enter into a contract and complete it according to his/her bidding that has been done. This is a form of screening to separate serious bidders and also prevent them from withdrawing after receiving the contract.

5. Foreign Bank Guarantee
This is applied in international trade, where the bank mobilizes a guarantee for one of its clients to benefit another country. For companies working with foreign partners, it is critical as a guarantee of payment or performance across borders.
6. Deferred Payment Guarantee
This assurance is used in deals where payment involves delay; ensuring that the payments will be made on the agreed future date. This is a common practice in many long-term loans.
7. Performance Bond
Like the performance warranty, this bond is given to guarantee that a project or a contract will be completed. Where the terms of a contract are not fulfilled by the bank, an amount as a penalty is paid to the project owner.
8. Shipping Guarantee
This allows the importer to assume control of items before they are accompanied by shipping documents. The bank ensures that the documents will be properly filed and presented, preventing someone else from receiving the goods.
What is a Letter of Credit?
An LC is an important financial tool used in international trading, which serves as a secure form of payment between the buyer and seller. A letter of credit is a form of guarantee from an issuing bank or other financial institution that the seller will receive payment within the agreed-upon time frame and at the correct amount provided if all conditions outlined in this LC are fulfilled. In these cases, the parties to international transactions are usually unacquainted and may not be subjected to the same system of laws as well as doing business under different sets. The LC acts as a bridge of trust: the seller is guaranteed to receive payment as the bank agrees to pay once specific conditions are met, such as the production of certain documents including shipping and export documents.
In applying the LC to a buyer with his bank, he is required to describe in detail details of goods being traded for and payment basis plus specific terms that must be met before release. The LC issued by the bank is forwarded to the seller’s bank and becomes a binding document. The seller ships the goods and provides to its bank all documents required under the LC, which are then closely checked for consistency with the stipulations of this document. If all goes well, the seller’s bank sends a payment request to the buyer’s Bank which makes such a payment. This system greatly minimizes the perils of international trade since both parties involved enjoy a high security level and in such an environment, the seller is only paid after fulfilling his part while the buyer has certainty that he/she pays for a properly fulfilled order.
Types of Letter of Credit
There are different types of letters-of-credit (LCs) directed to solve specific needs and risks in international trade, as well as finance. These categories can help businesses make the perfect selection of suitable ones for their transaction.
Here are the main types of Letters of Credit -
1. Revocable vs Irrevocable Letters of Credit
- Revocable LC - It may be modified or terminated without warning by the issuing bank to the beneficiary. Because of its security weakness, it is hardly ever used for international trade.
- Irrevocable LC - Can not cancel or modify without the consent of all parties involved, including a beneficiary. This form provides greater stability and is widely applied in global operations.
2. Confirmed vs Unconfirmed Letters of Credit
- Confirmed LC- It includes an additional warrant by another bank often located in the seller’s country. This implies that both the issuing bank and the confirming bank guarantee its payment.
- Unconfirmed LC- Secured only by the issuer. The seller is relying on the bankability of its buyer.
3. Sight vs Usance (or Time) Letters of Credit
- Sight LC - It must be paid to the beneficiary by presenting and checking copies of required documents.
- Usance (or Time) LC - Allows for a deferred payment. The seller gets paid after a particular time of the submission period for the necessary documents as stipulated in LC.

4. Transferable vs Non-Transferable Letters of Credit
- Transferable LC - Permits the payee (usually an intermediary) to convey some or all of his rights to another party, usually the actual supplier of goods.
- Non-Transferable LC -The LC rights are non-assignable. However, the payment can be made only to a specified beneficiary.
5. Standby vs Back-to-Back Letter of Credit
- Standby LC - Acts more as a bank guarantee. It is an alternate payment channel through which the bank settles due only when it fails to service its financial commitments or contractual obligations.
- Back-to-Back LC - It incorporates two LCs used in pairs, the second of which is based on its predecessor security. It is helpful in mediated transactions.
6. Red Clause vs Green Clause Letter of Credit
- Red Clause - It has a special provision that enables the beneficiary to receive an advancement of funds before delivering goods or services.
- Green Clause - It is analogous to the Red Clause but with a supplementary reference for storage charges on goods before shipping.
Bank Guarantee and Letter of Credit in International Trade
In international trade, Bank Guarantees and Letters of Credit play important roles in managing the risk to ensure a smooth deal across borders. A Bank Guarantee can be considered as a safety net that guarantees the benefit On the contrary, a Letter of Credit is directed to eliminate payment issues and have sellers obtain their money as per terms provided for in LC upon meeting all requirements. This certainty is critically important in international trade where the distances, distinguishable laws, and by their very nature uncertainties of dealing with new partners are huge challenges. These two instruments, through ensuring different aspects of a transaction, play their role in creating trust between parties and establishing easy international trade flow patterns.
FAQs :
1. What is the main difference between a Bank Guarantee and a Letter of Credit?
A Bank Guarantee assures the seller that the bank will pay if the buyer defaults. A Letter of Credit, on the other hand, guarantees the exporter’s payment as long as shipping documents meet the agreed terms.
2. Which is safer for exporters: Bank Guarantee or Letter of Credit?
For exporters, a Letter of Credit (LC) is usually safer because payment is assured once shipment documents are verified. A Bank Guarantee benefits the buyer more, as it protects them in case the exporter fails to deliver.
3. When should businesses use a Bank Guarantee instead of a Letter of Credit?
Businesses often use a Bank Guarantee for long-term projects, contracts, or government tenders where performance assurance is needed. A Letter of Credit is better for international trade transactions, where payment security is the top priority.
4. Can a Bank Guarantee be converted into a Letter of Credit?
No, a Bank Guarantee and a Letter of Credit are separate financial instruments. However, some businesses may use both together in high-value contracts to balance risk between buyer and seller.
5. Which option is more cost-effective: Bank Guarantee or Letter of Credit?
Generally, Bank Guarantees are less expensive compared to Letters of Credit. LCs involve multiple banks and documentation, which increases processing costs.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between a Letter of Credit and a Bank Guarantee is essential for businesses, especially those engaging in international trade. While both serve as vital financial tools to mitigate risks, their applications and implications vary greatly. Businesses must carefully consider their specific needs and the nature of their transactions to choose the most suitable instrument.
Share On:

Anurag Jain
Anurag Jain, is the co-founder and Executive Director of KredX. An IIT Kanpur alumnus and a techie-turned-entrepreneur with two decades of experience in the financial services sector, he drove business growth in companies like HSBC, Oracle, and Tavant Technologies, before co-founding KredX, in 2015. You can connect with him on LinkedIn to know more.



