Export Credit Insurance vs. Letter of Credit: Which is Right for Your Global Trade?
8/29/2023
Share on:
Explore the vital distinctions between Export Credit Insurance (ECI) and Letter of Credit (LC) in global trade financing. Learn how ECI mitigates risks, while LC provides payment security. Understand the factors influencing your choice and make informed decisions for international success.
Key Takeaways
- Export Credit Insurance (ECI) and Letter of Credit (LC) are vital financial instruments for global trade financing, but they serve different purposes and have distinct features.
- Export Credit Insurance (ECI) keeps you safe from risks like non-payment, political issues, and currency problems. It's like a big protective shield for exporters.
- A Letter of Credit (LC), on the other hand, is quite secure in terms of payment. It makes it safer for everyone concerned by ensuring that you will be reimbursed after certain requirements are met.
- The choice between ECI and LC is based on factors such as your level of risk tolerance, money management technique, and desired level of payment security.
- ECI offers more flexibility in negotiating payment terms with buyers, while LC involves strict adherence to predetermined conditions.
- Consider consulting financial experts or trade advisors to make an informed decision based on your specific global trade financing needs.
- Understanding the nuances of these financial instruments empowers businesses to make strategic choices that align with their international expansion goals.
In the intricate world of global trade, where businesses navigate through a complex web of international transactions, two financial instruments stand out as key players: Export Credit Insurance and Letter of Credit. These tools provide crucial support to exporters, acting as a safety net and streamlining cross-border transactions. However, when it comes to determining the right choice for your global trade, comprehending their intricacies is vital. In this article, we will dive into the realm of Export Credit Insurance and Letter of Credit, examining their functions, advantages, and limitations. By the conclusion, you'll gain a clearer understanding of which financial instrument best aligns with your global trade financing requirements.
Export Credit Insurance
Exporters can be insured against all sorts of potential risks related to international trade by using export credit insurance, often known as trade credit insurance. These risks include of foreign clients ignoring payments, political unrest, currency fluctuations, and insolvency problems. This is how it goes:
Benefits of Export Credit Insurance for Exporters
Export credit insurance benefits exporters by safeguarding them against payment risks, political instability, and currency fluctuations, enhancing financial security and global trade opportunities.
1. Risk Mitigation
Export Credit Insurance shields exporters from the uncertainty of whether they will receive payment for their goods or services. This risk mitigation ensures a more predictable cash flow, allowing businesses to plan and operate with confidence.
2. Cash Flow Stability
In the world of global trade, cash flow is king. Export Credit Insurance provides a safety net by covering losses from non-payment, helping businesses maintain a steady flow of funds to support their operations.
3. Expansion Opportunities
With the assurance of getting paid, businesses can explore new markets and expand their global footprint. Export Credit Insurance acts as a growth catalyst, encouraging businesses to take calculated risks.

Drawbacks and Limitations
While Export Credit Insurance offers substantial benefits, it's not without its limitations. For instance, depending on the insurer and the policy chosen, the coverage may change. Additionally, it doesn't offer a Letter of Credit's level of payment security. Certainly, here are more drawbacks and limitations of export credit insurance -
1. Costs
While export credit insurance provides protection, it comes at a price. Premiums can be relatively high, especially for high-risk markets or industries, impacting the overall cost-effectiveness of the policy.
2. Coverage
Limits Policies often have coverage limits, which means they might not cover all your sales. If your business expands rapidly or enters new markets, you may find your coverage insufficient.
3. Exclusions
Certain events may not be covered, such as wars, civil unrest, or deliberate contract breaches. It's crucial to understand what events are excluded from your policy.
4. Complex Claims Process
Filing a claim can be a complex process, involving extensive documentation and investigations. This can lead to delays in receiving compensation, impacting your cash flow.
5. Impact on Customer Relationships
Insisting on credit insurance may give the impression that you lack trust in your customers. This could potentially strain relationships, especially in long-term partnerships.
6. Premium Determinants
Premiums are often based on factors beyond your control, such as the political and economic stability of the buyer's country. This can lead to unpredictable costs
7. Availability
In some markets, export credit insurance may be challenging to obtain, limiting your options for risk mitigation.
Understanding these limitations can help you make informed decisions about whether export credit insurance is the right choice for your business.
Letter of Credit (LC)
A letter of credit is a type of financial instrument that banks use to guarantee payments to exporters if certain requirements are met. The LC serves as a middleman and ensures that they are paid, provided that the exporter follows its rules and conditions. Here's how the letter of credit works:
Step 1: LC Application
The LC process begins when the buyer (applicant) submits a request for an LC to their bank. This request includes details such as the LC type, amount, and terms.
Step 2: Issuing the LC
Upon receiving the application, the issuing bank assesses the applicant's creditworthiness and, if approved, issues the LC to the beneficiary (seller).
Step 3: Shipment and Documentation
The beneficiary ships the goods to the buyer and prepares the required documents, including the invoice, bill of lading, and packing list, in compliance with the LC terms.
Step 4: Presentation of Documents
The beneficiary presents the documents to their bank, known as the advising bank, which verifies their authenticity.

Step 5: Examination by Issuing Bank
The advising bank forwards the documents to the issuing bank, which reviews them to ensure they comply with the LC terms.
Step 6: Payment
If the documents are in order, the issuing bank makes the payment to the beneficiary, thereby fulfilling the LC obligation.
Step 7: Buyer Receives Goods
With payment secured, the buyer can claim the shipped goods from the carrier and proceed with their importation.
Benefits of Letter of Credit for Exporters
Letter of credit (LC) offers exporters enhanced payment security, guaranteeing that they receive payment when specified conditions are met, reducing risks and enabling smoother international trade.
1. Payment Security
The primary advantage of an LC is the assurance of payment. The bank is expected to make the payment whenever the exporter satisfies the requirements stated in the LC (such as submitting the necessary documentation). By doing this, the possibility of non-payment is reduced.
2. International Trade Facilitation
Letters of Credit are widely accepted in international trade. They provide a standardized and secure method of payment, reducing uncertainties for both exporters and importers.
3. Risk Reduction
LCs also mitigate risks for exporters by ensuring that payment is guaranteed as long as they comply with the LC terms. This reduces exposure to credit risks associated with overseas buyers.
Drawbacks and Limitations
Despite its advantages, LCs can be complex and involve higher costs compared to Export Credit Insurance. Additionally, discrepancies in documents can lead to delays in payment. Here are some drawbacks and limitations associated with a line of credit:
1. Interest Costs
One of the primary limitations is the interest cost. Borrowing from a line of credit often comes with interest payments, which can add up, especially if the balance remains high.
2. Creditworthiness
Your ability to secure a line of credit depends on your creditworthiness. If you have a poor credit history, you might not qualify for favorable terms or any credit line at all.
3. Variable Interest Rates
Unlike some fixed loans, lines of credit often have variable interest rates. This means your interest costs can fluctuate, potentially making it harder to predict and manage your finances.
4. Repayment Requirements
Lines of credit usually have minimum monthly payments. Failing to meet these requirements can negatively impact your credit score and financial health.

5. Risk of Overborrowing
The ease of accessing funds through a line of credit can lead to overborrowing and accumulating more debt than you can manage.
6. Secured vs. Unsecured
Secured lines of credit are backed by collateral, which could be your assets. Failing to repay a secured line could result in the loss of your collateral.
7. Reduced Credit Availability
As you use your line of credit, the available credit decreases. This reduced availability might affect your financial flexibility when you need it most.
8. Renewal Challenges
Some lines of credit have a set term, after which they must be renewed or renegotiated. If your financial situation changes unfavorably, you may struggle to renew or secure a new line.
9. Fees and Charges
Lines of credit may come with various fees, such as annual fees, transaction fees, or early closure fees, which can increase the overall cost of borrowing.
10. Complexity
Managing a line of credit can be more complex than a traditional loan. Keeping track of your borrowing, interest rates, and payment schedules can be challenging.
11. Potential for Revocation
Lenders can often change the terms of a line of credit or revoke it entirely, potentially leaving you in a tight spot.
It's essential to consider these drawbacks and limitations carefully when deciding whether a line of credit is the right financial tool for your needs.
Comparison of Export Credit Insurance and Letter of Credit
To make an informed decision about which financial instrument suits your global trade financing needs, let's compare Export Credit Insurance and Letter of Credit side by side:
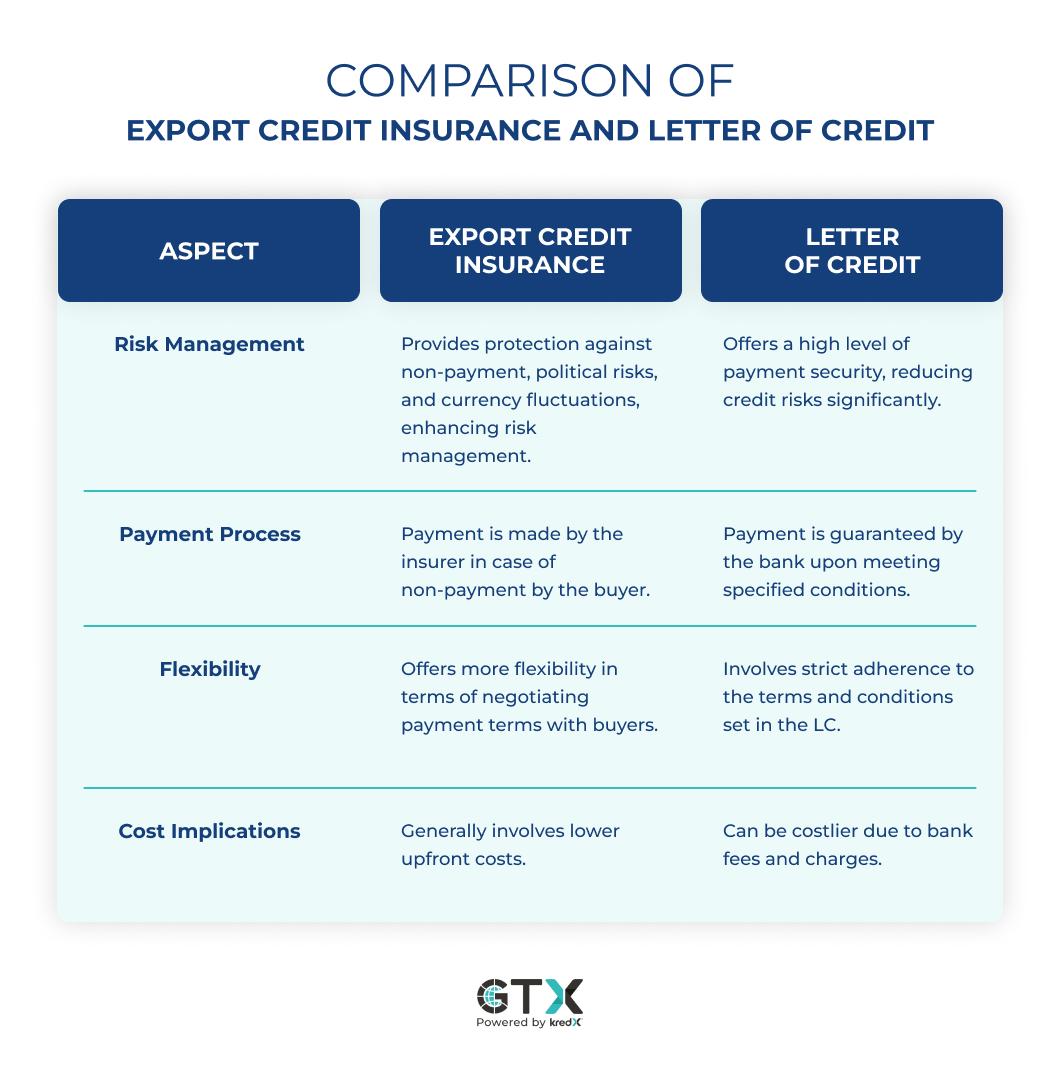
These are some of the key differences between Export Credit Insurance and Letter of Credit, and businesses should consider these factors when deciding which financial instrument best suits their global trade financing needs.
Conclusion
In the world of international trade, the choice between Export Credit Insurance and Letter of Credit can significantly impact your business's financial stability and risk management. Both instruments offer unique advantages, but they cater to different needs and circumstances. By carefully assessing your requirements and considering the factors mentioned, you can confidently choose the financial tool that aligns with your global trade financing goals
For businesses expanding into the global market, making the right choice between Export Credit Insurance and Letter of Credit is a strategic decision that can pave the way for international success.
Share On:

Saddam Hussain
Saddam Hussain is a digital marketing and supply chain finance expert with over a decade's working experience. He specializes in areas such as invoice discounting, working capital management, cash flow forecasting, and risk mitigation and is passionate about sharing his knowledge and expertise with others. His writing is clear, concise, and accessible to both finance professionals and business owners. He believes supply chain finance is a crucial component of any successful business. His goal is to empower readers with the knowledge and tools they need to achieve these goals. When he's not writing or consulting, he enjoys traveling and trying new foods. You can reach him through LinkedIn or Twitter for a quick chat.



