Global trade financing is a cornerstone of the modern business world, allowing enterprises to spread their reach across boundaries and tap into diverse markets. Effective payment procedures are critical to the success of these endeavors because they control the flow of funds, reduce risks, and build confidence among trading partners. In this comprehensive book, we will investigate the numerous payment mechanisms that power global trade financing, diving into both old methods and rising digital innovations.
Common Global Trade Financing Payment Techniques
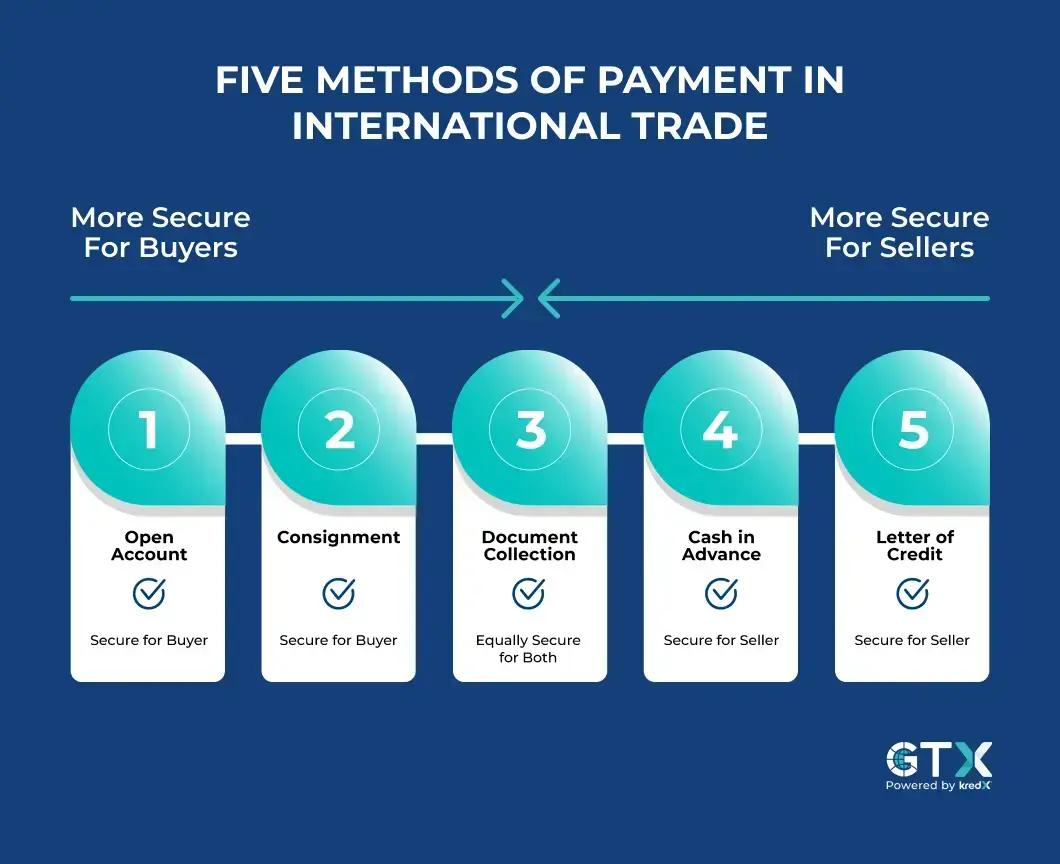
1. Letter of Credit (LC)
A Letter of Credit (LC) is one of the most commonly utilized payment techniques in global trade financing. This strategy ensures the exporter that payment will be made if certain requirements are met. A Letter of Credit entails the cooperation of banks representing both the importer and the exporter, assuring a secure transaction. The LC reduces risk for both parties since the exporter is assured of payment and the importer obtains assurance that products or services will be supplied as agreed.
While LCs provide security and trust, they are also difficult. The procedure entails rigorous documentation, conformity to terms, and obedience to rules. LCs, on the other hand, provide a robust payment mechanism that instills confidence in trading relationships for organizations engaged in high-value or complex international transactions.
2. Open Account
In an open account payment scenario, the exporter ships products or provides services to the importer before receiving payment. This strategy is primarily reliant on trust between trading partners and existing ties. While open account transactions are less complex and more flexible, they also pose more dangers to exporters. Importers, on the other hand, profit from postponed payments and less financial burden upfront.
3. Advance Payment
Advance payment is a simple procedure in which the importer pays in advance before the products are dispatched. This strategy is appropriate for situations in which confidence between trading partners is still developing. While it provides security to the exporter, it exposes the importer to the risk of non-delivery or delays. Advance payment is frequently employed in situations involving customized items or one-of-a-kind products.

Advanced Global Trade Financing Payment Techniques
1. Documentary Collections
Documentary collections serve as an intermediary payment mechanism in which banks facilitate the transaction. The exporter provides shipping documentation to their bank, which passes them to the importer's bank. The documents are given to the importer upon payment or acceptance of a draught. This strategy provides a halfway ground between open accounts and LCs, giving some security but requiring less documentation than LCs.
Documentary collections, on the other hand, are fraught with complications and risks. The exporter gives up control until payment is made, and the importer has some say in the process. Document discrepancies or disputes might cause payment delays or conflicts.
2. Bank Guarantees
Bank guarantees are financial commitments provided by banks on their client's behalf. These guarantees ensure that payment or performance obligations are met. Bid bonds, performance guarantees, and advance payment guarantees are all examples of bank guarantees. They give both parties engaged in the transaction assurance.
Bank guarantees, while effective, can involve cost and necessitate collateral or credit lines from the customer. They are especially beneficial in situations where non-payment or non-performance risks must be minimized, adding a degree of protection above and beyond typical payment methods.

Digital Payment Innovations in Global Trade Financing
1. Blockchain-Based Payments
Emerging technologies such as blockchain have made an impact on global trade finance. Blockchain provides a safe, transparent, and decentralized transaction platform. Its immutability lowers fraud and provides a verifiable transaction trace. This is especially useful in industries with complex supply chains and a large number of players.
The potential of blockchain resides in the creation of smart contracts that automate payment release upon meeting predefined conditions. This simplifies transactions, eliminates administrative burdens, and fosters trust among trading partners. Several trade finance platforms and consortia are investigating blockchain's potential to revolutionize global trade financing.
2. Digital Wallets and Mobile Payments
Digital wallets and mobile payment apps have grown in demand for cross-border transactions. These features make payments easier, more accessible, and faster. They cater to the digitally connected global economy and are especially advantageous for e-commerce transactions.
Digital wallets allow for rapid remittances and allow companies to enter international markets without the barriers associated with traditional banking systems. These methods are in line with the changing demands of modern customers and enterprises, and they provide efficient cross-border payment options.
Conclusion
Global trade financing payment methods are the foundation of international business. Businesses have a variety of alternatives, ranging from classic techniques such as letters of credit and open accounts to innovative digital solutions such as blockchain-based payments and digital wallets. The shifting landscape of global trade financing necessitates that organizations be knowledgeable about these strategies and adapt to changing preferences and technical improvements. Businesses can optimize their financial strategy, reduce risks, and assure successful cross-border trade transactions by understanding the peculiarities of each technique.
Share On:

Saddam Hussain
Saddam Hussain is a digital marketing and supply chain finance expert with over a decade's working experience. He specializes in areas such as invoice discounting, working capital management, cash flow forecasting, and risk mitigation and is passionate about sharing his knowledge and expertise with others. His writing is clear, concise, and accessible to both finance professionals and business owners. He believes supply chain finance is a crucial component of any successful business. His goal is to empower readers with the knowledge and tools they need to achieve these goals. When he's not writing or consulting, he enjoys traveling and trying new foods. You can reach him through LinkedIn or Twitter for a quick chat.



