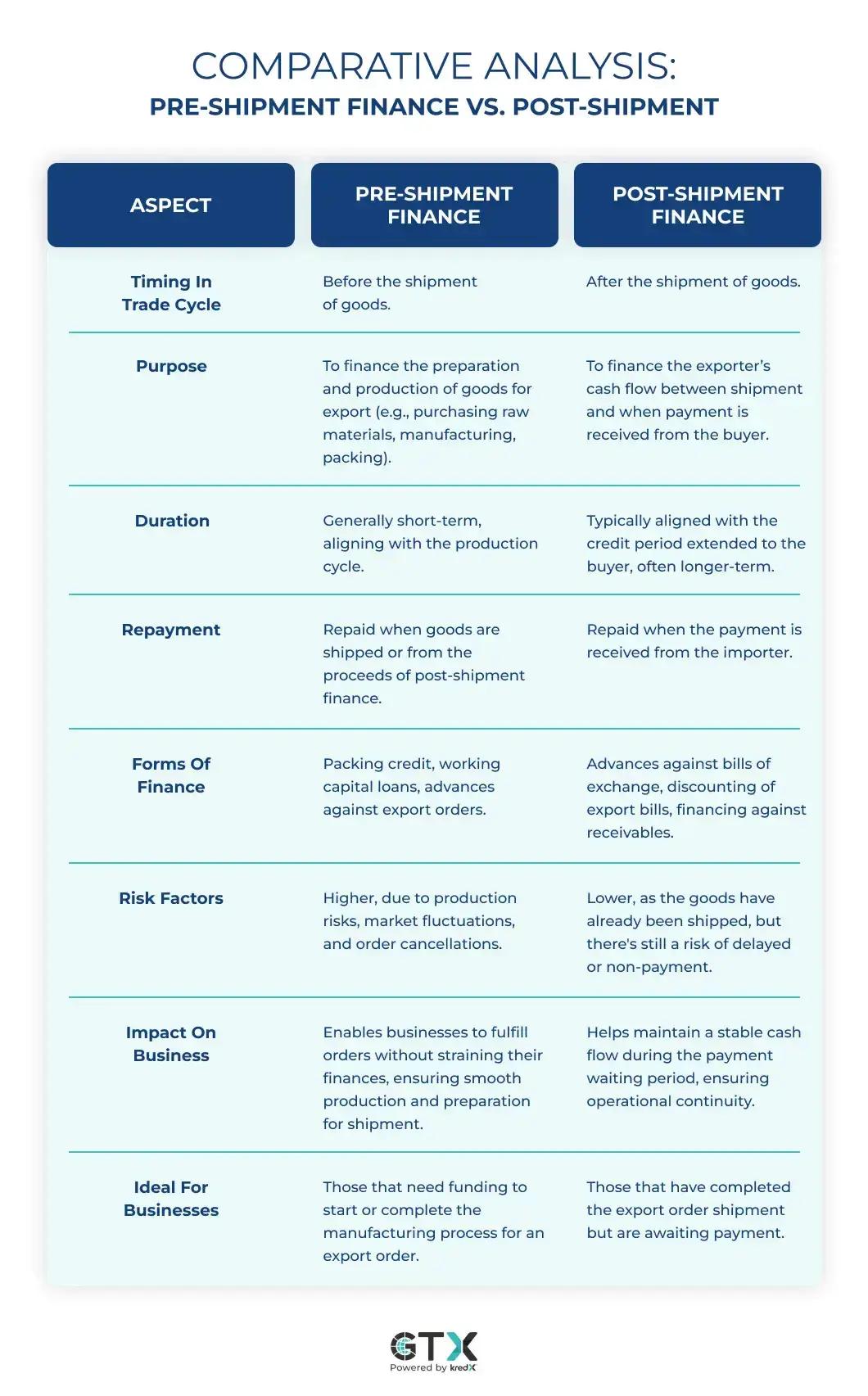
What Are the Key Differences Between Pre-Shipment and Post-Shipment Finance?
1/15/2024
Share on:
In international trade, efficient financial management is critical for the success and sustainability of export operations. Two key elements in this financial landscape are pre-shipment and post-shipment finance. Both play pivotal roles at different stages of the export process, offering crucial support to exporters. Understanding the distinctions between them is vital for businesses engaged in global trade to manage their financial resources effectively.
What is Pre-Shipment Finance?
Pre-shipment finance is a crucial financial tool exporters use to fund the preparation and processing of goods before they are shipped overseas. This type of financing is essential for covering various costs, including the purchase of raw materials, production, packaging, and transportation of the products intended for export. The primary goal of pre-shipment finance is to provide exporters with sufficient working capital so they can fulfill orders without straining their finances. It plays a pivotal role in ensuring that exporters are not financially burdened during the critical phase between receiving and shipping an order.
What is Post-Shipment Finance?
Post-shipment finance is a type of funding provided to exporters after they have shipped the goods but before they receive payment from the buyer. This form of finance is crucial in international trade, as it helps exporters manage their cash flow during the time lag between the shipment of goods and the receipt of payment. When goods are shipped, exporters often have to wait for a significant period before receiving payment, especially if the terms of sale include a credit period extended to the buyer. During this interval, the exporter might face a cash crunch, as their capital is tied up in the shipped goods yet to be paid for. Post-shipment finance addresses this challenge by offering financial support during this waiting period.
Comparative Analysis: Pre-Shipment Finance vs. Post-Shipment
Risks in Pre-Shipment and Post-Shipment Finance
For exporters, pre-shipment finance is like getting a financial head-start. It helps cover costs before your goods hit the international market. But, this early support comes with its challenges:
- Production Pitfalls
Think of this as preparing for a big launch but facing unexpected delays. Supply chain hiccups, labor challenges, or technical issues in production can set you back.
- Market Uncertainties
The demand for your products might shift, prices could change, or new trade laws might emerge, impacting the success of your orders.
- Cancellation Concerns
What if your buyer cancels after you've already started production? This leaves you with costs that might be hard to reclaim.
- Asset Value Risks
Since this finance is often linked to the value of your export order or materials, any drop in their value can hit your finances.

After shipping your goods, post-shipment finance steps in to help you manage finances until the payment arrives. However, this waiting period has its risks:
- Payment Delays
In international trade, payment delays are common, especially with extended credit periods. This can tighten your cash flow and affect your business operations.
- Risk of Non-Payment
There is a risk the buyer may delay in making payments, or worse default on payments completely due to various reasons such as bankruptcy, lack of cash flow, or other such reasons.
- Goods Rejection Risks
If the buyer isn’t satisfied with the goods or if they get damaged in transit, it could lead to disputes and further delay your payment.
- Receivable Risks
If your finance is secured against future payments (receivables), any problems in collecting these payments can pose a financial challenge.
- Global Instabilities
Political changes or economic shifts in the buyer's country can affect the payment process, adding another layer of uncertainty.
As an exporter, understanding and preparing for these risks in both pre-shipment and post-shipment finance is crucial. It’s all about balancing financial support with cautious risk management to ensure your business thrives globally.
Financial Products and Instruments
Types of financial products available for Pre-shipment finance
Packing Credit
This is the most common form, offering finance specifically against export orders. Exporters use it primarily for procuring raw materials and covering manufacturing costs.
Overdraft Facility
Banks may provide an overdraft facility based on the exporter's creditworthiness, allowing them to overdraw from their account up to a certain limit for export-related expenses.
Export Working Capital Loan
This is a loan specifically designed to fund the entire cycle of an export transaction, from procurement to shipment.
Advance Against Incentives Receivable
Exporters can also get advances against government subsidies and incentives due to their export activities.
Types of financial products available for post-shipment finance

Export Bill Discounting
This involves selling the exporter’s bills of exchange or invoices at a discount to the bank before the buyer pays them.
Export Bill Negotiation
Under a letter of credit arrangement, banks can provide funds against the submission of shipping documents.
Advance Against Export Bills Sent on Collection
Finance provided against bills sent to the importer on a collection basis.
Factoring and Forfaiting
These involve selling export receivables at a discount to a factoring company, which then takes on the responsibility of collecting payment from the buyer.
How Pre-Shipment and Post-Shipment Finance Affects Business Cash Flow and Operation?
Pre-shipment finance improves cash flow by providing the necessary funds to start production without tapping into the company’s working capital. It enables businesses to take on larger orders than they could with their capital alone, thus supporting business growth and operational expansion.
Post-shipment finance ensures steady cash flow even when there’s a delay between shipment and payment, helping businesses meet their ongoing expenses. It allows exporters to offer more competitive payment terms to buyers, such as extended credit periods, enhancing their market competitiveness.
Criteria for Eligibility for Pre-Shipment Finance
- A confirmed export order or letter of credit from a credible buyer.
- Good credit history and a satisfactory relationship with the financing institution.
- Compliance with the export policy and other regulatory requirements.
Criteria for Eligibility for Post-Shipment Finance
- Proof of shipment like shipping documents.
- An export invoice representing the sale.
- A track record of compliance with previous credit agreements.
Conclusion
Both pre-shipment and post-shipment finance are integral in facilitating international trade, enabling exporters to expand their business, manage cash flows effectively, and compete globally. Understanding and leveraging these financial instruments can significantly influence the success and sustainability of businesses engaged in international trade.
Share On:

Anurag Jain
Anurag Jain, is the co-founder and Executive Director of KredX. An IIT Kanpur alumnus and a techie-turned-entrepreneur with two decades of experience in the financial services sector, he drove business growth in companies like HSBC, Oracle, and Tavant Technologies, before co-founding KredX, in 2015. You can connect with him on LinkedIn to know more.



